Scanning, Analyzing and Refreshing Metadata
Once a library has been created, it is processed by Komga so all the files are matched to series and books, and metadata is gathered. As time goes on, you’ll add and remove books to the libraries or make other changes that mean the library is no longer up-to-date. You can Scan libraries to bring them up-to-date. Scanning, Analyzing and Refreshing a library do different things.
Scan Library Files
Scanning a library makes Komga check its folders and sub-folders for new or removed books. If it finds new media, it then pulls it into the library. You can think of scanning as “check for new or changed content”.
All files that have changed after a scan will be Analyzed.
You should Scan Library Files if you have:
- Added or deleted files or folders
- Renamed a file or folder
- Moved files or folders from one location to another
By default, Komga will scan your libraries regularly.
Deep scan
This will force the scanner to compare all scanned books with the ones stored in the database. Normally this is not required, as Komga uses the last modified time of the parent folders to decide whether to compare books, but some filesystems may behave differently.
Trigger a Deep Scan if Komga is missing some books after a scan.
What happens during a Scan?
Komga will generate a library representation of your files on disk. A Komga library does not represent exactly your folder structure.
- Komga will create a Series for each subfolder of any library, whatever the depth of this subfolder in your directory structure
- Komga will create a Book for each file found, and place it inside the Series corresponding to the parent folder of the file
Analyze books
Analysis is automatically performed when content is added to your Library. In rare cases, new versions of Komga may update the media analysis capabilities to correct something or add the ability to detect new things. In those cases, content may be re-analyzed when you access it after the new server version is installed.
What happens during Analysis?
Whenever an item is added to one of your Libraries, Komga performs some analysis on it to gather information. In addition, all files analyzed will also be refreshed for metadata.
Gather media properties
The primary purpose of media analysis is to gather information about that media item. All of the media you add to a Library has properties that are useful to know, such as:
- Container: ZIP, RAR, EPUB, PDF, etc.
- Images Format: JPEG, PNG, WEBP, etc.
Why, though? What use are these media properties? Your Server, together with your apps, can use this information to help determine whether (and how) content can be played.
For example: Imagine you have a CBR file with WEBP images, but you’re using Internet Explorer (which can’t read WEBP). Since the webreader knows what kind of content your browser can display and since your media analysis detected that the book has WEBP images, your Komga Server can convert those images to a compatible format (like JPEG) for you in order to let you read your book successfully.
Generate default artwork
During analysis, artwork will automatically be grabbed from a book file. The first page will be used for poster/thumbnail type purposes.
Analyze your content
You can analyze content in multiple ways: for a book, for a series, or even for an entire Library.
Look for the action menu icon ![]() and click on Analyze.
and click on Analyze.
Depending on the size of your Library, analysis may take a while.
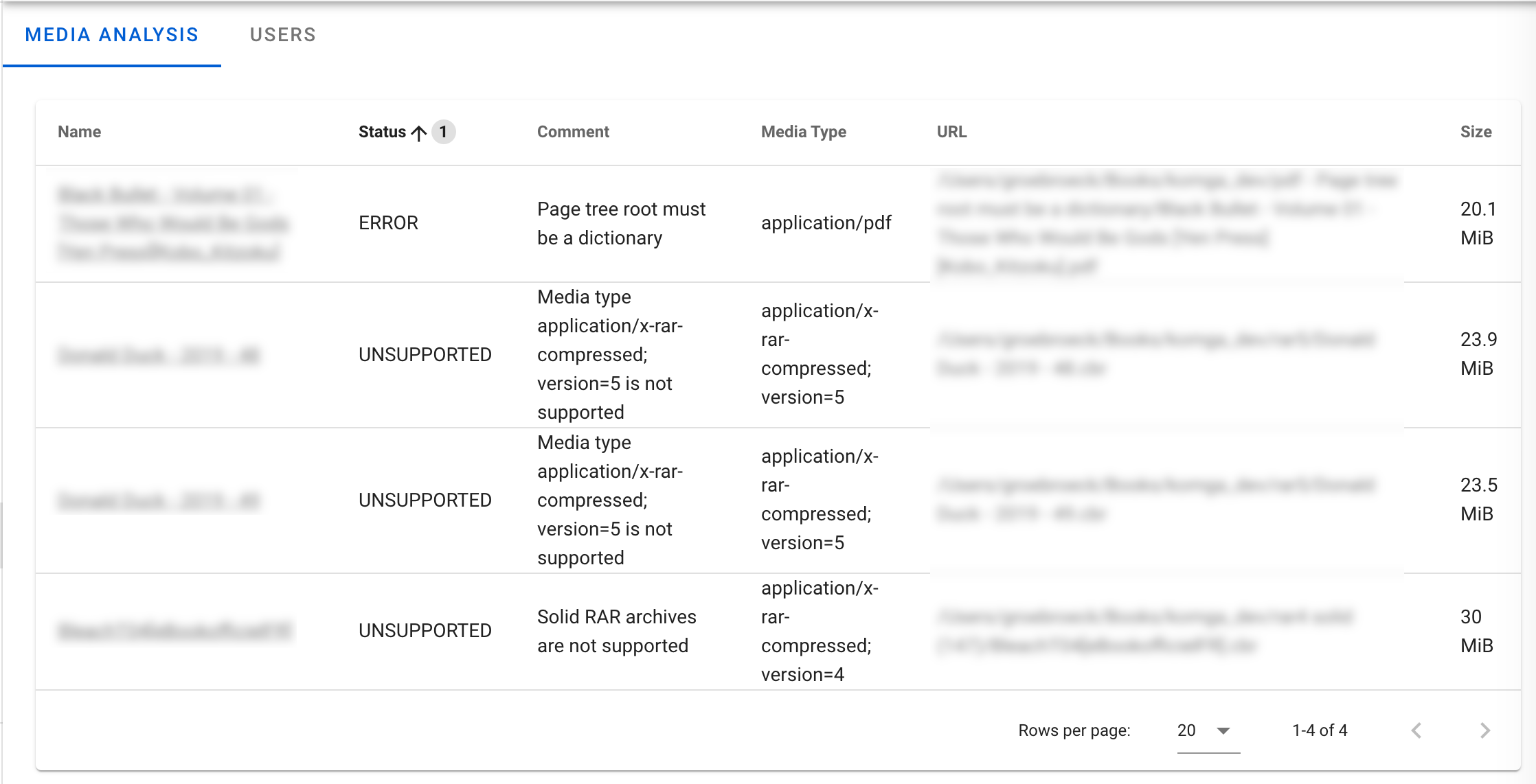
Media Analysis screen
You can check all the media for which the analysis did not succeed from the Media Analysis screen. You can access it from Media Management > Media Analysis.
It will show you all books with a status of:
- Error: Komga could not analyze the book. If possible, there will be a comment to describe the error.
- Unsupported: Komga does not support those files. The comment will give you more information.
Refresh metadata
Refreshing Metadata for a library, series, or individual book causes the metadata for the item to be refreshed, even if it already has metadata. You can think of refreshing as “update metadata for the requested item even if it already has some”.
You should refresh a library or individual item if:
- You’ve changed options for the library
- You’ve added "local media assets" (such as artwork)
Metadata is gathered from the following sources:
- a local
ComicInfo.xmlfile located inside a CBZ or CBR - the metadata of an EPUB file
- local media assets
The metadata refresh is dependent of the options of the Library.
Import metadata for CBR/CBZ containing a ComicInfo.xml file
Book metadata
This will import the following elements from the ComicInfo.xml file in Komga:
Year,Month, andDayto form the Release DateWriter,Penciller,Inker,Colorist,Letterer,CoverArtist,Editor, andTranslatoras Authors with the according role. A value with multiple names separated by a,will be split in different authors.Title,Summary,Numberas their Komga equivalent- Valid
Weblinks as a book link - The
Tagselement will be split by,and added to the book's tags - If the
GTINelement contains a valid ISBN, as the book's ISBN
Series metadata
This will import the following elements from the ComicInfo.xml of the Series' books in Komga:
- The
SeriesandVolumeelements will be used to overwrite the title of the Series, in the form<Series> (<Volume>), or just<Series>if theVolumeelement is not present, if theVolumeis1, or if Append volume to series title is disabled. If multiple values are present, the most frequent value from all books will be used. - The various
AgeRatingvalues will be converted to a number in Komga. The highest value from all books will be used. - The most frequent
Publishervalue will be used as Komga's equivalent. - A
Mangaelement with the valueYesAndRightToLeftwill mark the reading direction as Right to left. The most frequent value from all books will be used. - The
Genreelement will be split by,. All genres from all books will be added to the Series. - The
LanguageISOelement will be used as the Series' language. The most frequent value from all books will be used. - The highest value from
Countwill be used as the total count of books.
Collections
The SeriesGroup element will be split by , and used to create collections with those names, or add the series to an existing collection if it exists.
If the SeriesGroup element is set to different values in each book of the series, then each value of the elements will create a collection.
Read lists
The AlternateSeries or StoryArc elements will be used to create a read list with that name, or add the book to an existing read list with that name.
If the AlternateNumber element is set, it will be used to position the book in the read list.
StoryArcNumber
If the StoryArcNumber element is set, it will be used in conjunction with StoryArc to position the book in the read list.
Both StoryArc and StoryArcNumber elements can contain multiple values, separated by ,. Komga will do its best to match each pair:
- If both elements are set, but do not contain the same number of values, the extra values will not be used
- If there are invalid values, like blank strings or invalid numbers, the whole pair will be ignored
Import metadata from EPUB files
Book metadata
This will import the following fields from the Epub metadata in Komga:
dc:titleelement as the Titledc:descriptionelement as the Summarydc:dateelement as the Release datedc:identifierelement as the ISBN, if it is a valid ISBNdc:creatorelement as Authors. The role will be imported either from theopf:roleproperty, or from ametaelement containingroleproperty and amarc:relatorsscheme. A value with multiple names separated by a,will be split in different authors.- the meta property
belongs-to-collectionrefined asgroup-positionwill be used as the book Number and Number Sort
Series metadata
This will import the following fields from the Epub metadata in Komga:
dc:publisherelement as the Publisherdc:languageelement as the Language- The
page-progression-directionproperty of thespineelement as the Reading direction - The
belongs-to-collectionmeta property will be used to overwrite the title of a Series. If multiple values are present, the most frequent value from all books will be used.
Import metadata generated by Mylar
Mylar can generate a series.json file inside your Series folders. This option will import the following fields into Komga:
- The
namefield will be used for the Series title. If thevolumefield is set and is different from1, then theyearfield will be appended to the title, in the form<name> (<year>). statuswill be used to set the Series status.description_formattedordescription_textwill be used for the Series summary.publisherwill be used for the Series publisher.age_ratingwill be used for the Series age rating.total_issueswill be used for the total count of books.
Import local media assets
Local artwork
This will enable import for local artwork, check the Local Artwork Assets section for more information.
Import ISBN within barcode
ISBN barcode
Komga will inspect the first and last 3 pages of each book for barcodes. If a barcode is present and contains an ISBN code, it will be imported.